For Leg Length Imbalances Podiatrists Prefer Shoe Lifts

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this condition is very easily solved, and can reduce numerous cases of back problems.
Therapy for leg length inequality commonly consists of Shoe Lifts. These are low-priced, typically being below twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 and up. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Lumbar pain is the most common health problem afflicting people today. Over 80 million people have problems with back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem that costs businesses millions of dollars yearly because of lost time and output. Fresh and improved treatment solutions are constantly sought after in the hope of decreasing the economical impact this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world experience foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts might be of very helpful. The lifts are capable of easing any pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous experienced orthopaedic orthopedists.
So as to support the body in a well balanced fashion, your feet have got a very important task to play. In spite of that, it is often the most overlooked region of the body. Many people have flat-feet meaning there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other areas of the body like knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that ideal posture and balance are restored.
Contracted Toes
 Overview
Overview
A Hammer toes is a toe that is bent because of a muscle imbalance around the toe joints. The imbalance causes the toe to bend at one or more joints, pushing the middle of the toe upward in a claw-like position. If you notice such changes, it is important to seek proper treatment. Hammer toes never get better without some type of intervention and the sooner it is treated, the better the outcome.
Causes
While most cases of hammertoes are caused by an underlying muscle imbalance, it may develop as a result of several different causes, including arthritis, a hereditary condition, an injury, or ill-fitting shoes. In some cases, patients develop hammertoes after wearing shoes or stockings that are too tight for long periods of time. These patients usually develop hammertoes in both feet.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
If you have any of these symptoms, do not assume it is due to hammer toe. Talk to your doctor about symptoms such as a toe that curls down, corns on the top of a toe, calluses on the sole of the foot or bottom of the toe, pain in the middle joint of a toe, discomfort on the top of a toe, difficulty finding any shoes that fit comfortably, cramping in a toe, and sometimes also the foot and leg, difficult or painful motion of a toe joint, pain in the ball of the foot or at the base of a toe.
Diagnosis
Hammer toes may be easily detected through observation. The malformation of the person's toes begin as mild distortions, yet may worsen over time - especially if the factors causing the hammer toes are not eased or removed. If the condition is paid attention to early enough, the person's toes may not be permanently damaged and may be treated without having to receive surgical intervention. If the person's toes remain untreated for too long, however the muscles within the toes might stiffen even more and will require invasive procedures to correct the deformity.
Non Surgical Treatment
You should seek medical advice if you have a hammer toe. Here are some things you can do in the meantime. None of these things will cure the hammer toe, but they may relieve the pain and discomfort. Only wear shoes that are high and broad across the toes. There should be at least 1.5 cm of space between your longest toe and the tip of the shoe. Keep in mind that this could be either your big toe or your second toe. Don't wear heels higher than 5 cm. Wear the appropriate shoe for the activity you are doing. You can buy non-medicated hammer toe pads. They fit around the pointy top of the toe joint and help relieve painful pressure. Gently massaging the toe may help relieve pain. Put ice packs wrapped in cloth on the hammer toe to reduce painful swelling.
Surgical Treatment
Hammer toe can be corrected by surgery if conservative measures fail. Usually, surgery is done on an outpatient basis with a local anesthetic. The actual procedure will depend hammertoe on the type and extent of the deformity. After the surgery, there may be some stiffness, swelling and redness and the toe may be slightly longer or shorter than before. You will be able to walk, but should not plan any long hikes while the toe heals, and should keep your foot elevated as much as possible.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hallux Valgus?
Overview
 A bunion (a.k.a Hallux Valgus) is a common foot condition associated with a prominent bump on the inside of the forefoot (see Figure 1). The word bunion? comes from the Greek root for the word turnip. Bunions can lead to discomfort over the prominence, especially if patients wear tight fitting shoes. It is common for bunions to run in family? and gradually increase over time. The vast majority of bunions can be managed successfully with basic non-operative treatment. Surgery is reserved for patients who have persistent symptoms in spite of appropriate non-operative treatment.
A bunion (a.k.a Hallux Valgus) is a common foot condition associated with a prominent bump on the inside of the forefoot (see Figure 1). The word bunion? comes from the Greek root for the word turnip. Bunions can lead to discomfort over the prominence, especially if patients wear tight fitting shoes. It is common for bunions to run in family? and gradually increase over time. The vast majority of bunions can be managed successfully with basic non-operative treatment. Surgery is reserved for patients who have persistent symptoms in spite of appropriate non-operative treatment.
Causes
Bunions most commonly affect women. Some studies report that bunions occur nearly 10 times more frequently in women. It has been suggested that tight-fitting shoes, especially high-heel and narrow-toed shoes, might increase the risk for bunion formation. Bunions are reported to be more prevalent in people who wear shoes than in barefoot people. While the precise causes are not known, there also seems to be inherited (genetic) factors that predispose to the development of bunions, especially when they occur in younger individuals. Other risk factors for the development of bunions include abnormal formation of the bones of the foot at birth (congenital), nerve conditions that affect the foot, rheumatoid arthritis, and injury to the foot. Bunions are common in ballet dancers.
Symptoms
No matter what stage your bunion is in, you can be in pain. Though bunions take years to develop, you can experience pain at any stage. Some people don?t have bunion pain at all. Pain from a bunion can be severe enough to keep you from walking comfortably in normal shoes. The skin and deeper tissue around the bunion also may become swollen or inflamed.
Diagnosis
X-rays are the best way to determine the amount of deformity of the MTP joint. Blood work may be required to rule out other diseases that may be associated with bunions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Other tests such as bone scans or MRI's are not usually required.
Non Surgical Treatment
Long-term treatment of bunions must be directed towards re-balancing the foot, so that we no longer walk with our weight forced on to the inner border of the foot. This is accomplished by controlling and reducing pronation with the use of a high quality arch support or custom made orthotics. These devices comfortably re-balance the feet and overcome pronation. This reduces the abnormal weight forces on the big toe and its metatarsal head, allowing the feet to function normally. As a result, the deformity should not worsen, and the pain should gradually subside. If the foot is not re-balanced, the deformity and pain will become worse. 
Surgical Treatment
In 2010, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) published guidance about a minimally invasive surgical procedure to treat bunions. The aim of the procedure is to repair the tilting of the big toe. The technique can be carried out under a local anaesthetic or a general anaesthetic, using X-rays or an endoscope for guidance. The type of endoscope used will be a long, thin, rigid tube with a light source and video camera at one end. One or more incisions will be made near the big toe so that bone-cutting instruments can be inserted. These will be used to remove the bunion and to divide one or more bones located at the front of the foot. Wires, screws or plates will be used to keep the divided bones in place. After the procedure, you may need to wear a plaster cast or dressing to keep your foot in the correct position until the bones have healed. You may be given a special surgical shoe that enables you to walk on your heel. As the procedure is relatively new, there's little in the way of reliable evidence regarding its safety or effectiveness.
Prevention
To minimize the chance of developing bunions, never force your feet into shoes that don?t fit. Choose a shoe that conforms to the shape of your foot. Opt for shoes with wider insteps, broad toes, and soft soles. Shoes that are short, tight, or sharply pointed should be avoided.
Partial Achilles Tendon Rupture Rehabilitation Time
Overview
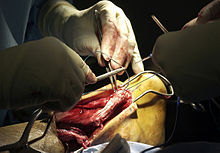 About two thirds of all Achilles tendon ruptures occur during sports. Total ruptures are most common in sports with stop-and-go movements, especially ball sports. The majority of patients suffered a ruptured Achilles tendon when stopping suddenly during a fast vigorous movement. Usually the Achilles tendon tears about 5 cm before it inserts into the heel bone. Particularly at risk for a tear are athletes who have already suffered from Achilles tendon problems for some time.
About two thirds of all Achilles tendon ruptures occur during sports. Total ruptures are most common in sports with stop-and-go movements, especially ball sports. The majority of patients suffered a ruptured Achilles tendon when stopping suddenly during a fast vigorous movement. Usually the Achilles tendon tears about 5 cm before it inserts into the heel bone. Particularly at risk for a tear are athletes who have already suffered from Achilles tendon problems for some time.
Causes
The most common cause of a ruptured Achilles' tendon is when too much stress is placed through the tendon, particularly when pushing off with the foot. This may happen when playing sports such as football, basketball or tennis where the foot is dorsiflexed or pushed into an upward position during a fall. If the Achilles' tendon is weak, it is prone to rupture. Various factors can cause weakness, including corticosteroid medication and injections, certain diseases caused by hormone imbalance and tendonitis. Old age can also increase the risk of Achilles' tendon rupture.
Symptoms
If you rupture your Achilles tendon, you may hear a snapping or popping sound when it happens. You will feel a sudden and sharp pain in your heel or calf (lower leg). It might feel like you have been kicked or hit in the back of your leg. You may also have swelling in your calf. be unable to put your full weight on your ankle, be unable to stand on tiptoe, or climb stairs, have bruising around the area. If you have any of these symptoms and believe you have ruptured your Achilles tendon, go straight to accident and emergency at your local hospital. If you partially rupture your Achilles tendon, the tear may only be small. Symptoms of pain and stiffness may come on quite suddenly like a complete rupture, but may settle over a few days.
Diagnosis
In diagnosing an Achilles tendon rupture, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask questions about how and when the injury occurred and whether the patient has previously injured the tendon or experienced similar symptoms. The surgeon will examine the foot and ankle, feeling for a defect in the tendon that suggests a tear. Range of motion and muscle strength will be evaluated and compared to the uninjured foot and ankle. If the Achilles tendon is ruptured, the patient will have less strength in pushing down (as on a gas pedal) and will have difficulty rising on the toes. The diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture is typically straightforward and can be made through this type of examination. In some cases, however, the surgeon may order an MRI or other advanced imaging tests.
Non Surgical Treatment
There is no definitive protocol for conservative management. Traditionally, conservative treatment involved immobilisation in a cast or boot, with initial non-weight bearing. Recently, good results have been achieved with functional bracing and early mobilisation, and it is common to be immediately weight-bearing in an orthotic. Conservative management reduces the chance of complications, such as infection. There is a risk the tendon can heal too long and more slowly. 
Surgical Treatment
Surgery offers important potential benefits. Besides decreasing the likelihood of re-rupturing the Achilles tendon, surgery often increases the patient?s push-off strength and improves muscle function and movement of the ankle. Various surgical techniques are available to repair the rupture. The surgeon will select the procedure best suited to the patient. Following surgery, the foot and ankle are initially immobilized in a cast or walking boot. The surgeon will determine when the patient can begin weight bearing. Complications such as incision-healing difficulties re-rupture of the tendon, or nerve pain can arise after surgery.